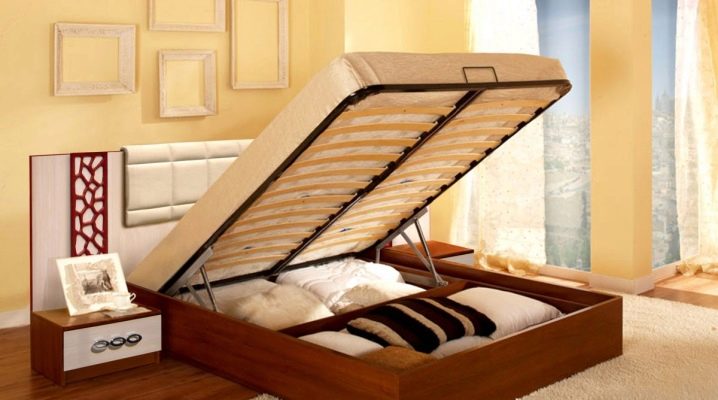
Slats for bed
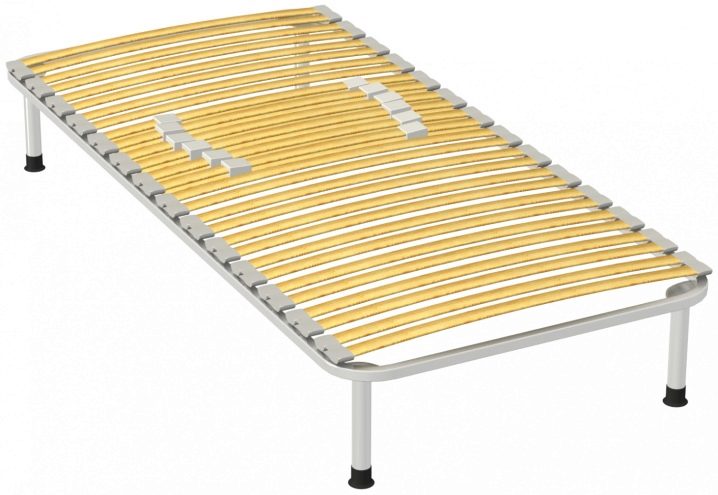
Beds with springs have long since disappeared and modern models with an orthopedic base have replaced them. Their design is like two drops of water similar to each other and it consists of a wooden box, a metal frame and one or two rows of slats - curved panels. The latter are responsible for the orthopedic properties of the bed and take on the weight of the mattress and the person resting on it. What are the slats for beds and what are their advantages over the spring - let's look into the article.
What it is?
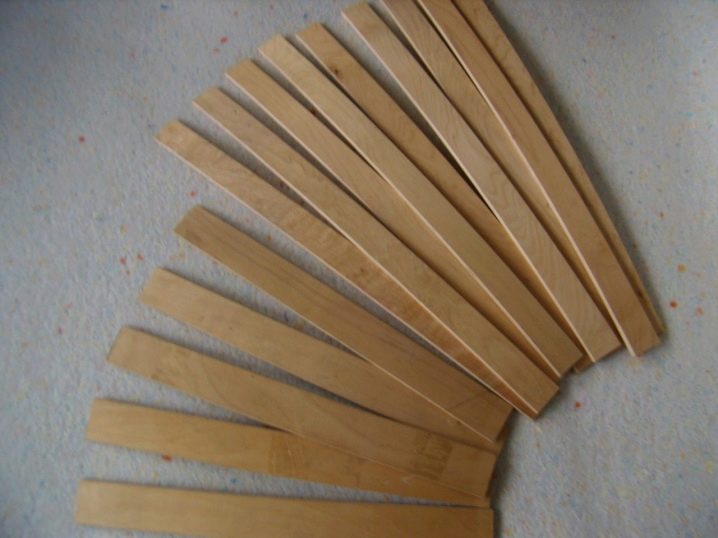
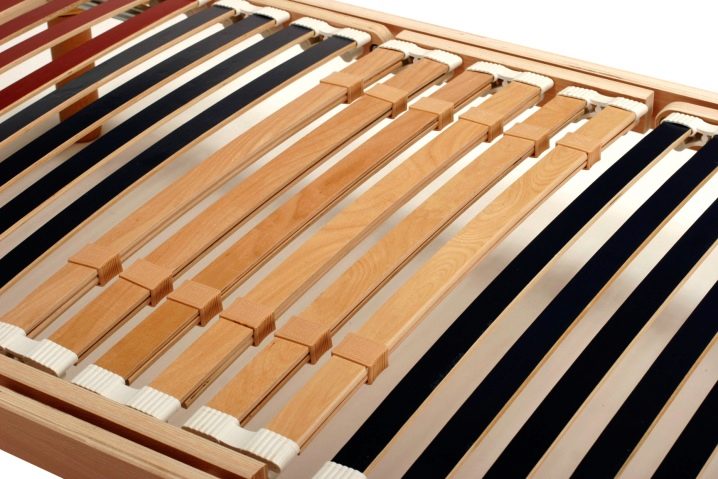
Slats are wooden plates, panels that make up the foundation of any modern bed. Their feature is a curved C-shape and the ability to withstand a large weight of a mattress + person. Reiki can be made from:
- Birch - ductile and accessible material;
- Lindens - inexpensive analogue;
- Beechwood;
- An ash tree;
- Maple tree.
Birch lamellae, or armor - the most popular and affordable orthopedic slats. Beech and ash details are more expensive and are usually installed in beds of 100% solid wood.
Why do we need?
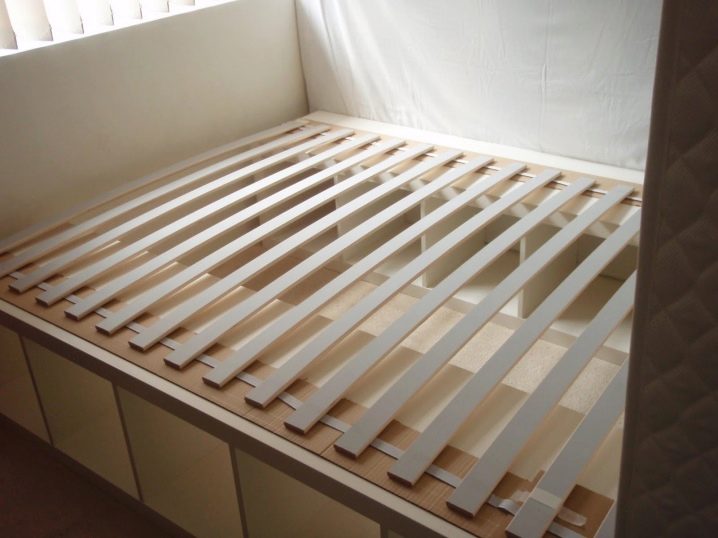
The orthopedic base of the bed is assembled like a puzzle - from a couple of dozens of lamellae and a common metal frame that holds them together. Wooden strips create a slatted bottom on which an orthopedic mattress is placed. Modern models of mattresses do not tolerate uneven and dubious surfaces and are rather heavy in their weight, and the slats, in turn, provide:
- Natural ventilation for the mattress due to the small distance between each of them;
- Reducing the load on the mattress and on the bed box;
- Increase the anatomical effect of the mattress, that is, complement its orthopedic properties;
- They create a light springy effect due to their curved shape, so this base does not creak or emit other annoying sounds;
- Extend the life of the bed, because they fully assume the weight of the mattress.
No wonder the slatted bed base is called orthopedic: it evenly distributes the load on the resting spine,providing the quality and full sleep.
Slats allow the mattress to "breathe" and remove moisture from it. Each new mattress we wrap in a waterproof mattress topper, which can create a real greenhouse effect inside it. The slatted bottom eliminates this problem, and the orthopedic “friend” continues to serve us faithfully for decades.
In what form can I buy?
Slats are sold as part of an orthopedic foundation in a bed and separately - individually. Like any other element of the bed, they are subjected to stress and can break. The experts do not recommend sleeping on a bed without even one lamella: firstly, the load on the other details of the bed increases and their integrity is questioned, secondly, the orthopedic properties of the mattress and the base are reduced, which are designed to evenly distribute the load on the spine and ensure healthy sleep.
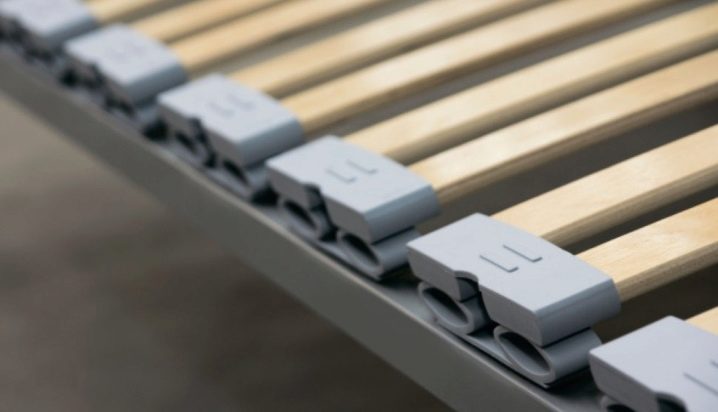
Lamellas are sold individually or in a set according to the size of a bed or a sofa, so if one board is cracked or completely broken, it will not be difficult to replace it, it remains only to choose the right one in thickness and width.A set of slats can be sold on the ribbon if your bed uses this rack fastening system (it is, by the way, already outdated). Additionally, you will have to buy spare parts for mounting the slats: cap-holder (internal or invoice). There are component caps that hold the lamella and are attached to the metal base of the bed without "intermediaries".
Which is better?
Lamels are of two types: wide and narrow:
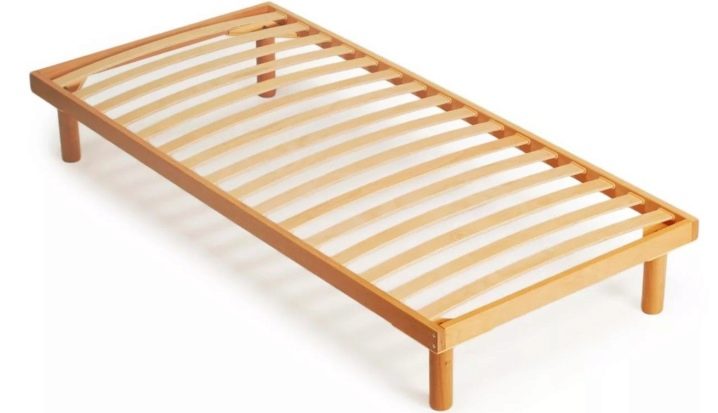
- Wide Lamellas about 900-1000 mm long are installed in the same row on the grid and are often used in single or single beds. Slats across the width of the bed are suitable for springless mattresses and models with “bonnel” springs.
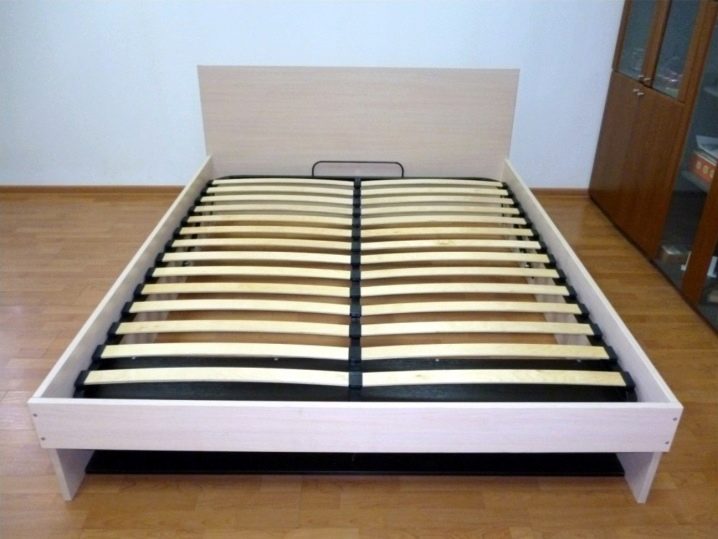
- Narrow (700-800 mm) are arranged in two rows - each for one bed. This type of lamella arrangement is recommended for mattresses with independent springs.
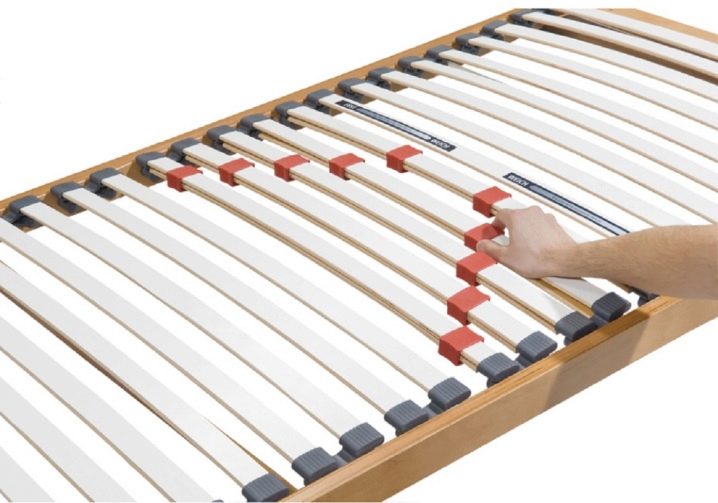
If we talk about the number of elastic panels, then the best option is 26-30 pieces for a double bed. For a single bed, the number of slats is half as much - 13-15 pieces. The greater the number of lamellas, the better: such a number of slats provides optimal flexibility of the base of the bed and can withstand more weight.
Lamels differ in thickness, length, width and distance that is formed between them. The optimal thickness of the slats is 8-10 mm, width - 5-7 cm, the length can vary from the width of the berth (140 cm, 160 cm, 180 cm - for each of them lamellas of different lengths are required). Between the lamellae there should be a distance of no more than the width of one of them - about 4-7 cm.
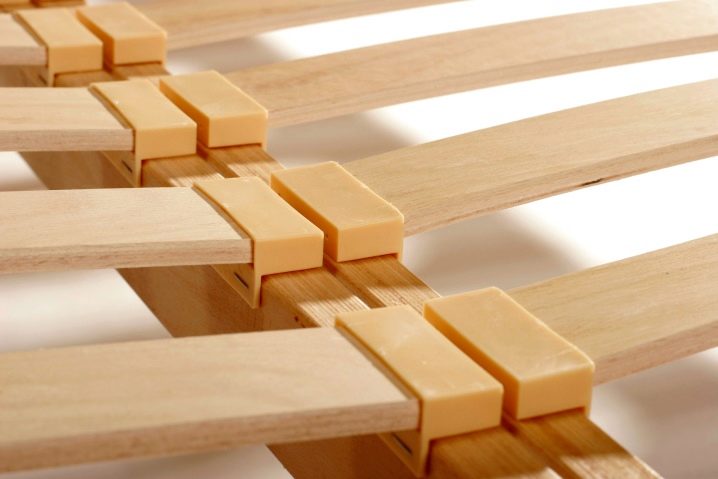
There is another important classification - according to the type of lamella holders. Modern manufacturers fix latoflexes on special holders from:
- Plastics;
- Rubber;
- Polypropylene.
Lamellae on a tape or mounted on a metal frame also move to the side, freeing up space for practical and easy fastening, which, in case of a rail break, allows you to replace the latter yourself.
You can not say which slats are better. If we talk about their fastening, it is better to choose rubber or polypropylene holders - they are stronger and more qualitative than plastic counterparts.
Dimensions
Beds vary in bed size, and for each of them will require a different length of lamellae. For a double bed 180x200 cm, lamellas with a width of 880/885 mm are suitable, for a single bed - 900-990 mm, provided that the lamellae are lined up in one row, and 500 mm for a couple of rows of rails.Lamellas can vary in size and even bend angle, so before replacing and buying a separate rail, it is important to measure the length and width of already installed parts in order to find exactly the same.
Lamels differ in width - 40, 50, 70, 80 mm, but their thickness is practically unchanged, the ideal is 8 mm.
How to choose?
When buying a bed with an orthopedic base or slatted bottom, pay attention to the number of those slats.
The more of them, the better - experts say. And the wider the bed, the greater the number of slats should be at its base.
The optimal number of slats on the bed grid is 20–22 pieces for a bed of 190–200 cm long. If there are more slats, then such a bed will be softer, more plastic and more functional, and will withstand the greater weight of the mattress. Reiki differ not only in quantity, but also in the material from which they are made.
The most accessible is birch, which is not inferior in its strength to harder wood species.
Birch slats are usually installed in beds "economy" and the middle segment. At the base of the beds from the array put beech slats - durable and solid slats. Give preference to rubber or semi-propylene rail holders; plastic wear out quickly and is not as practical to use.
When choosing a slatted bed base, pay attention to the distance between the slats: it should not be larger than the width of the slat. If it is large, then the springless mattress will fall into these “holes”, and the lamellas themselves will soon come out and in operation, since they will not be able to withstand a lot of weight.
When buying a double bed with a width of 140 cm and more, choose a model in which the rack bottom is divided into two halves. So for each berth will be created its own rack base. It is logical to assume that shorter strips are used in this type of bed.
Lamels, lined up in one row, suitable for single and single beds, folding beds and sofas, when there is no large load on the base.
How to do it yourself?
For the production of lamellae used natural wood - suitable birch or poplar. Making an orthopedic bed base and lamella with your own hands has a great advantage - you can choose the number of slats. This will require:
- Mounting rails or birch plywood 1.5-2 mm thick;
- Mounts for slats - rubber or polypropylene;
- Cutting tool.
The process of creating lamellas begins with a drawing and cutting slats of the same size along it.
To make work as simple as possible, choose smooth plywood from 100% birch without knots and rough edges, so that you do not have to process it additionally.
How to insert?
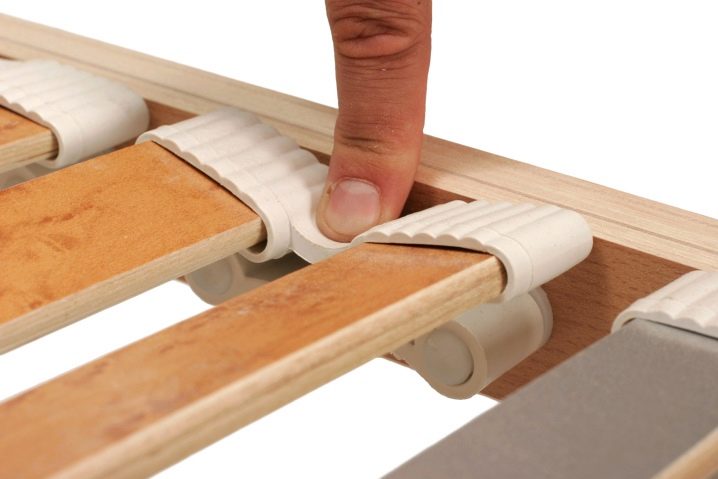
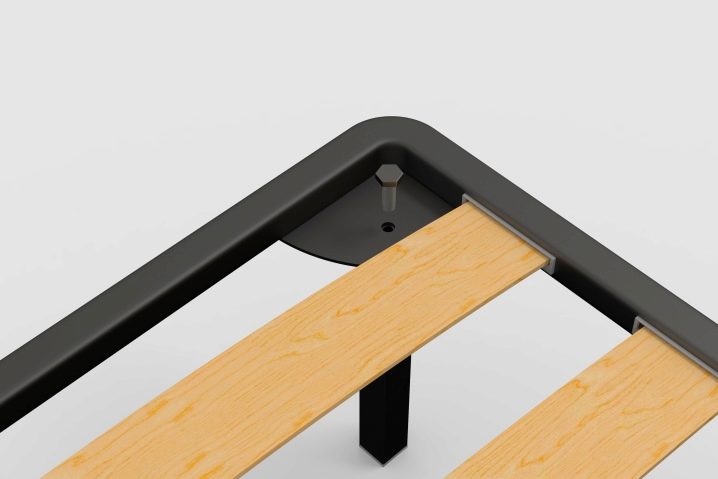
The slat is attached to the metal frame of the bed as follows: a special cap is put on it and, as such, they enter the hole (slot) at the base of the bed.
To remove the lamella or replace the damaged part by a whole, bend the bar and remove the mount from the socket. Remove intermediary caps from two sides and replace the last one with a whole new bar. Put the caps back on, insert one end of the lamella into the slot, bend it and place the other end in the hole on the other side of the frame.
To attach the part to the frame correctly, it will take a little effort and bend the bar: it will not break.
On how to install the slats on the bed, see the following video.
Grate or solid bottom?
Beds with lamellae at the base practically supplanted the usual spring models and beds with a solid bottom, because possess a number of essential advantages:
- Lamellae evenly distribute the load on the human spine during rest and sleep;
- Strengthen the effect of an orthopedic mattress;
- They assume its weight (which is sometimes very heavy). Do not think that it is the body of the bed that is subjected to the greatest load, no. She is taken by the very orthopedic base made of a metal body and a number of lamellae;
- Slatted bottom allows the mattress to "breathe", that is, it provides the correct air exchange and does not allow that to "suffocate". When buying a mattress, we often wear a waterproof cover on it, which does not let in either moisture or air, and the rack bottom saves it from direct death and ensures evaporation of moisture and “breathing” as a whole;
- The arcuate shape provides a light spring effect under load;
- The base with the lamellae does not creak even under heavy load (due to their shape and quantity);
- Reiki can be changed individually, if suddenly one of them is cracked or broken;
- The rack bottom is affordable and of higher quality than a solid counterpart.
Manufacturers of orthopedic mattresses are advised to choose a slatted bed base, because it additionally prolongs the life of the mattress.Depreciation, which "give" the bed curved slats positively affects the health of the person and his spine.
Another advantage in favor of the grille is that it is easy to replace a broken bar with a new one. And still lamels can be made independently of a plywood sheet. Such a minus of such a foundation can be called the need to turn the mattress every 3-4 months because of the rack bottom and the lack of support between them.
To prolong the life of the mattress, simply turn it over from time to time and enjoy a comfortable sleep.
The solid bottom of the bed is not that out of fashion. It simply faded into the background for the following reasons:
- The flat bottom does not allow the mattress to "breathe", and that, in turn, loses its orthopedic properties;
- If a crack or slight damage has formed on it, then the entire bottom will have to be replaced;
- A flat bottom does not have a positive effect on the health of the spine, which mattress you would not use - spring or modern type with independent springs.
By the way, mattresses with independent springs can be used only on the slatted bed base.