Subtleties of warming attic floor
In order not to heat the cold attic during the winter period, it is necessary to warm the attic floor of the room. Do not heat the attic, if it is not used for its intended purpose.
In order to resolve this issue, it is necessary to think about how to insulate the attic with the help of modern building materials. The process can occur both from inside the room and from the outside. Warming is performed in the process of complex repair before final finishing.
Even if the attic is not insulated during construction, you can always address this issue and carry out additional work.
Special features
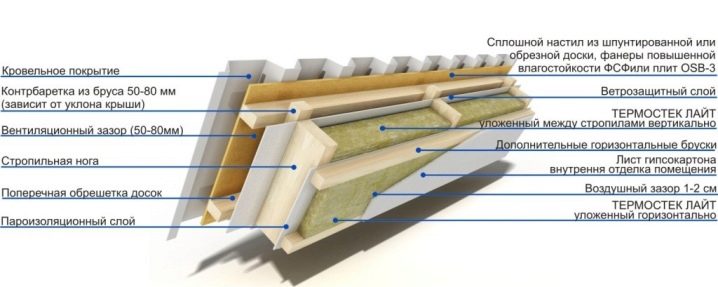
Most of the warm air masses go through the roof. Therefore, when building a house with a non-insulated attic, you need to carefully approach the topic of warming the attic floor with wooden beams. After all, it creates a certain barrier between warm rooms and cold attic space.
Consider the special criteria for thermal insulation of the attic, affecting the preservation of temperature in the house:
- Purpose of the room. The attic is a kind of buffer between the environment and the habitable rooms. His task is to regulate the temperature difference between the external environment and the house.
- Temperature mode. In any season and any day, the temperature of the air masses in the attic will always be higher than outside the window. That is why it is very cold in the attic in winter and unbearably hot and stuffy in summer.
- Heat loss in the winter. The more the substance is heated, the less dense it becomes. This is a physical phenomenon. That is why in residential premises with a heating system, warm air from home appliances is concentrated in the ceiling area. That is, if you do not warm the ceiling, then in winter all the warm air will warm the attic.
- Excessive heat in the summer. In summer you can observe the reverse process. The roof, heated by the rays of the sun, will heat the attic air, which, in turn, will penetrate the room through the attic floor.
- Reverse circulation of air masses. Coming in contact with the ceiling without heat insulation, warm air becomes cold, more dense and, as a result, falls to the floor.This is reflected in the living room in the form of walking drafts that are harmful to human health.
- The appearance of excess moisture. In contact with the non-insulated attic, moist hot air turns into condensate. The overall level of humidity in the house increases, which leads to the appearance of mold lesions in the corners.
- Saving. Heat, gone through the roof without insulation, is about 30%. This means that with proper insulation of the attic floor, you can save 30% of the fuel used. The use of air conditioning in the summer will also be associated with lower costs.
The entry of warm air masses into a technical attic (non-residential) leads to negative consequences:
- Due to the mixing of warm and cold masses in the attic can cause condensation. Water falling to the surface can lead to wood rotting processes on the bearing beams.
- If the attic is warm, then the snow gathered on the roof will begin to melt. The water dripping at the same time, will begin to turn into icicles. Formed frost on the drainage system.
It is best to choose insulation according to SNIP recommendations.
Materials
In order to choose the right type of insulation for the ceiling, you need to know a few factors. The heat insulator should not only have a low coefficient of thermal conductivity, but also have certain properties:
- Resistance to moisture and mechanical stress. The seal should not change its shape under mechanical loads. His qualities must remain unchanged, even in the case of wetting.
- Heat resistance. The material should not burn and sustain burning. High temperatures should not have a devastating effect on him.
- Low weight. To create a protective thermal frame you need to select materials with low weight. Then the attic floor will not be subjected to mechanical stress.
- The ability to pass steam. The accommodation must have an acceptable temperature and normal humidity. To ensure this, you need to choose only vapor-permeable finishing materials.
- Environmental factors. The heat insulator must comply with all sanitary and hygienic standards. Hypoallergenic and chemical neutrality are the basic requirements for the material.And also it should not contain toxic substances and volatile compounds.
- Mineral base. Insulation should not contain organic compounds, their basis should be polymers. This will prevent the appearance of mold and will not be eaten by mice.
Based on the foregoing, to insulate the attic woodwork, there are several popular types of insulation:
Mineral insulation
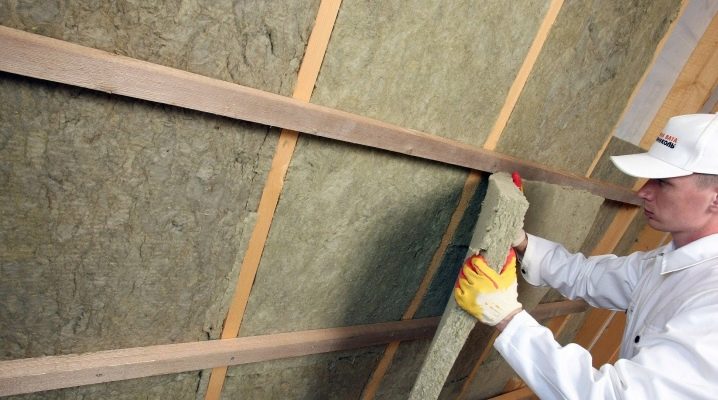
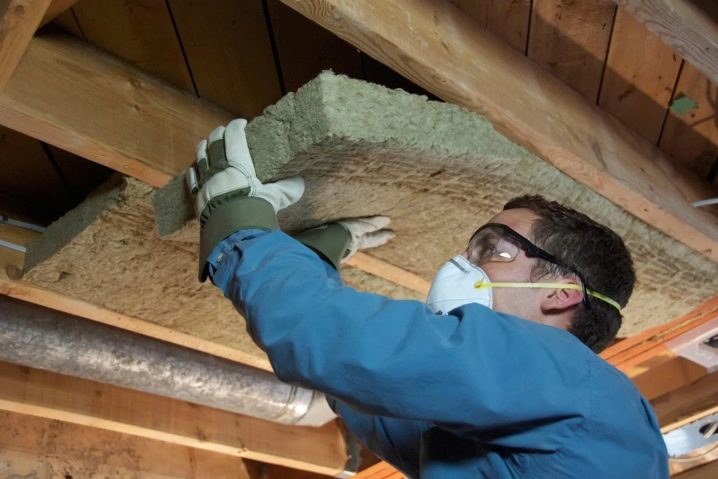
Mineral wool is made in two forms - roll and in mats. It is produced by melting rocks at very high temperatures. Basalt wool is the most suitable for attic insulation. It combines all the properties of a heat insulator. Mineral wool is quite light and fragile. To protect it from mechanical impact (push through, press it), wooden flooring is laid over the insulation.
The best type of insulation for these purposes will be a hard mat of high density, on the one hand reinforced with foil. It is laid with foil down. At the same time provides reflection of heat and have a vapor barrier.
Glass wool
The production technology of the material is very similar to the production of basalt wool.But molten glass is taken as the main component. It has good spring properties. But at the same time it is fragile. In terms of mechanical stress, it breaks. Glass wool is cheaper than mineral insulation, so it is suitable for those who are limited in the budget.
But it is necessary to take into account that when moisture enters its insulating properties deteriorate. It is harmful to humans, as small glasses damage the skin and can cause irritation.
Loose insulation
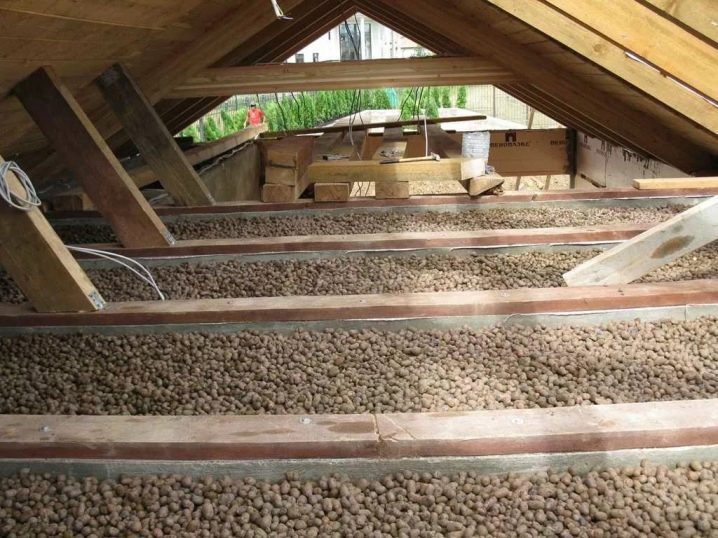
Expanded clay is rounded brown pebbles. They are made from certain types of red clay, which is sintered at a very high temperature. Claydite has a very low coefficient of thermal conductivity, since its structure consists of closed spheres. Each pebble is protected from moisture by the fact that there is a dense clay layer on its surface. Small pebbles of claydite are able to fill in hard-to-reach places, hidden cavities in bearing wooden elements.
This natural mineral heat insulator is not susceptible to burning, there are no harmful substances, there is no mold, and it does not like rodents.
Foam sheets
The heat insulator with polymer structure is produced by sintering small spherical granules. Its standard size is 100x100 cm. Thickness ranges from 1 to 15 cm. Polyfoam is one of the affordable and cheap insulants. But at the same time it has the lowest thermal conductivity. Since it consists of polymers, there is no organic matter in its composition. This means that it is moisture-resistant, does not rot, and does not form mold. The heat insulator is not exposed to fire, but under conditions of high temperature, it begins to emit toxic emissions and there is a risk of high smoke. The disadvantages of foam can be attributed to the fact that, due to its closed structure, it does not let water vapor through at all.
It is not recommended to warm the attic from the side of the living room with foam, as there is a risk of moisture accumulation.
Extruded polystyrene plates
The composition of the substances they are the same as foam, but the methods of their manufacture are radically different. Expanded polystyrene is obtained by hot extrusion, when a prepared polymer mixture is passed through a special apparatus.The specific density of the material is higher than that of the foam, its structure is porous and homogeneous. This leads to higher thermal conductivity. Insulation is strong and can withstand a large weight load.
Experienced builders recommend this material as insulation for attic floors.
PE foam with reflective foil
The construction name of the material is penofol. This insulation in the form of a roll, made of polyethylene foam, covered with foil. It can be combined with other types of heat insulators, since in itself it has a limited scope. The structure of closed pores gives a low coefficient of thermal conductivity. Through polyethylene does not pass air, liquid, water vapor. Therefore, penofol is a good hydro insulator. The foil plays the role of a reflector, that is, returns heat back to the living room. Its thickness is from 3 to 15 mm.
Chipboard for reinforced concrete slabs
This, above all, affordability and cheapness. They go as insulation for ceilings in barns, baths, farm buildings. The method of application is coating wooden attic structures with a mixture of clay and sawdust.Method, though primitive, but effective. Sawdust can be bought at the sawmill. Clay is also available. Knead the solution is not difficult. With a low specific weight, the mixture is very solid, especially after complete drying. Therefore, it does not load wooden floors. The material is vapor-permeable, but mold bacteria can develop due to sawdust, besides rodents like to spoil this type of insulation.
Most often, weatherization of concrete structures occurs minplitoy, mineral wool, chopped straw and opilkobetonom.
Scheme of work
First you need to prepare the insulating materials and tools:
- hammer;
- hacksaw;
- plane, chisel;
- drill and screwdriver;
- construction stapler;
- ruler, tape measure;
- ladder;
- wooden bars and planks;
- vapor barrier;
- finishing material.
To decide what insulation will be used:
- mineral wool;
- polystyrene foam;
- sawdust;
- penofol;
- glass wool;
- Styrofoam;
- expanded clay.
Then you should carry out the installation work.
Mounting technology
Depending on the choice of insulation and the method of laying.
Mineral insulation
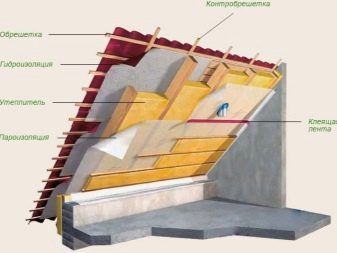
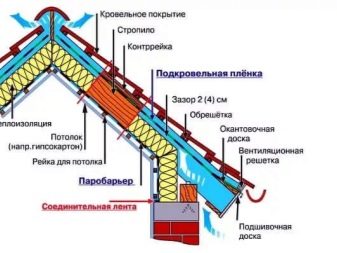
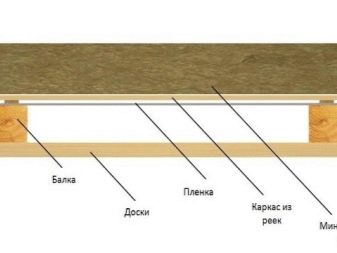
Cotton wool is laid in three ways: cells, grooves and a continuous layer.The choice depends on the degree of load. The best design is obtained from a continuous layer. First you need to lay a vapor barrier film. She removes water vapor, which is sent from the room to the attic. The film is laid strictly in accordance with the marking, lap. Wooden structures must be tightly covered with foil, otherwise they will rot.
At the second stage, wool is laid. This is a simple procedure, insulation is cut into strips. When laying you need to ensure that the insulation is not wrinkled, and between the sheets there were no gaps.
Attic floors must be waterproofed. Then lay a rough coating, which later will be the basis for finishing.
Polystyrene or extruded polystyrene foam
Laying hard insulation is quite simple. First you need to level the base, remove unevenness, drops on the floor. Put the cement-sand screed. Sheets are stacked between the bars. If no one lives in the attic, then the insulation must be closed with plastic film. And if the floor will be operated, then OSB must be put on the foam plastic or it must be poured with cement mortar.
Sawdust
First sawdust mixed with cement and water (10: 1: 1). This mixture is poured attic base. If it is non-residential, then sawdust is used without a frame, a device for strengthening. But with increased load, it is necessary to strengthen the base, otherwise the sawdust will hesitate. It is imperative to carry out the calculation and calculate the junction to the wall.
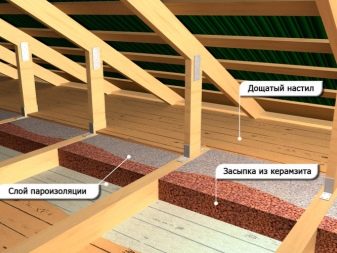
Expanded clay
The lack of insulation is that it is difficult to deliver to the place of installation. They fall asleep slabs and pie. At first the obreshetka is mounted, then the draft floor is put on it. The heat insulator is filled up and leveled with a rake. At the end everything is filled with cement mortar. With the first floor in a private house is better to work with such insulation.
Tips and tricks
For proper performance of work, use the advice of professionals:
- foiled insulation is laid with the shiny side down;
- it is better to lay a thin heat insulator in two layers, use a checkerboard pattern;
- during the work should be sealed joints;
- Since wood can rot, only vapor-permeable materials can be used with it in pairs (ruberoid in such cases cannot be used);
- when working with glass wool, you need to adhere to protection techniques (use gloves, glasses, masks);
- warming by polyfoam is not recommended to be combined with the wooden bases;
- the technical gap between the waterproofing layer and the heat insulator is from 20 to 50 mm;
- sheets of foam should be laid very tightly;
- all joints and each node must be filled with foam;
- joints of waterproofing film must be glued with adhesive tape;
- It is necessary to combine heat-insulating materials with each other in order to achieve the best result.
Today, there are several basic types of insulation for attic space. For each situation, you should choose your type of heat insulator. If you follow the instructions clearly, the work on weatherization will be done perfectly. In the work, you can use new types of insulation (ecowool). But for its installation will require special equipment.
See the following video for the correct weatherization of the attic floor.